Python for loop
In this python article, we will discuss how to iterate using the for loop with some examples.
1. for loop
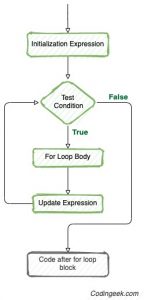
for loop is iteration statements, which allow a set of instructions to be performed repeatedly until a certain condition is fulfilled. Basically, we use it to iterate over elements from a list, string, dictionary etc.
As soon as we reach the last element it will skip the statement block and jump to the next statement.
Syntax: for variable_name in iterable: Statement-sequence
2. range() function
range() function is an in-built function in Python that is used to return a sequence of numbers.
Syntax: range(start , end , increment)
Default values of start and increment are 0 and 1 respectively.
So if we use range(5) – our loop will run for values 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
- Start(optional) defined the point, we want to start our sequence, by default 0
- End (Required) defines the last value of the sequence
- Increment (optional) defined how many steps or count we want to go at a time, by default 1
x = 12 for i in range(2, x, 2): print(i)
Output 2 4 6 8 10
Let’s see how we can access element from different iterators using for loop.
3. Looping through a list
We can access list element using loop through two ways:
- using
rangefunction and access the element of the list via index - without using the
rangefunction and directly access the elements
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7]
#using range() function
for i in range(len(x)):
print(x[i], end=", ")
print("")
#without using range() function
for i in x:
print(i, end=", ")Output 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7,
4. Looping through a string
Similar to the ways we access the list, we can access string elements using for loop.
x = "Codingeek"
#using range() function
for i in range(len(x)):
print(x[i], end=", ")
print("")
#without using range() function
for i in x:
print(i, end=", ")Output C, o, d, i, n, g, e, e, k, C, o, d, i, n, g, e, e, k,
5. Break Statement
Sometimes we do not need to loop through all the elements, so if we want to break the loop in-between then for that we use break keyword.
In the below example as soon as it counters the value of sum greater than 7 it will break the loop
sum = 0
for i in range(10):
if sum > 7:
break
sum += i
print(sum)Output 0 1 3 6 10
6. Continue statement
When we want to skip some part of the for loop just for that specific iteration and jump to the next iteration then we use the continue keyword.
In the below example as soon as it counters the value 5 then it will not print it and go to the next loop.
for i in range(7):
if i == 2:
continue
print(i)Output 0 1 3 4 5 6
7. Pass statement
We can’t write an empty for loop so instead of keeping it empty we write a pass keyword in it.
for i in range(5):
pass8. loop with else statements
Sometimes we want to do something only if the for loop finishes without breaking in between then we use else keyword.
This else block will execute only if the loop runs completely without a break.
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
for i in x:
print(i)
else:
print("Codingeek")
# breaking the loop in-between
# else block will not run
for i in x:
if i > 2:
break
print(i)
else:
print("Codingeek")
Output 1 2 3 4 Codingeek 1 2
9. Conclusion
In this article we learned about
- for loop
- break statement
- continue statement
- pass statement
- for loop with else block
Helpful Links
Please follow the Python tutorial series or the menu in the sidebar for the complete tutorial series.
Also for examples in Python and practice please refer to Python Examples.
Complete code samples are present on Github project.
Recommended Books



An investment in knowledge always pays the best interest. I hope you like the tutorial. Do come back for more because learning paves way for a better understanding
Do not forget to share and Subscribe.
Happy coding!! ?